Object Oriented Programming Notes
Lesson 2: Java Lab
- class header - consists of the class keyword and the name of the class
- integrated development environment (IDE) - a software application for writing, compiling, testing, and debugging program code
○ in our case, that would be Visual Studio Code
- software - a collection of instructions that is run by a computer
- source code - a collection of programming commands
- syntax - the rules for how a programmer must write code for a computer to understand
- syntax error - a mistake in the code that does not follow a programming language’s syntax
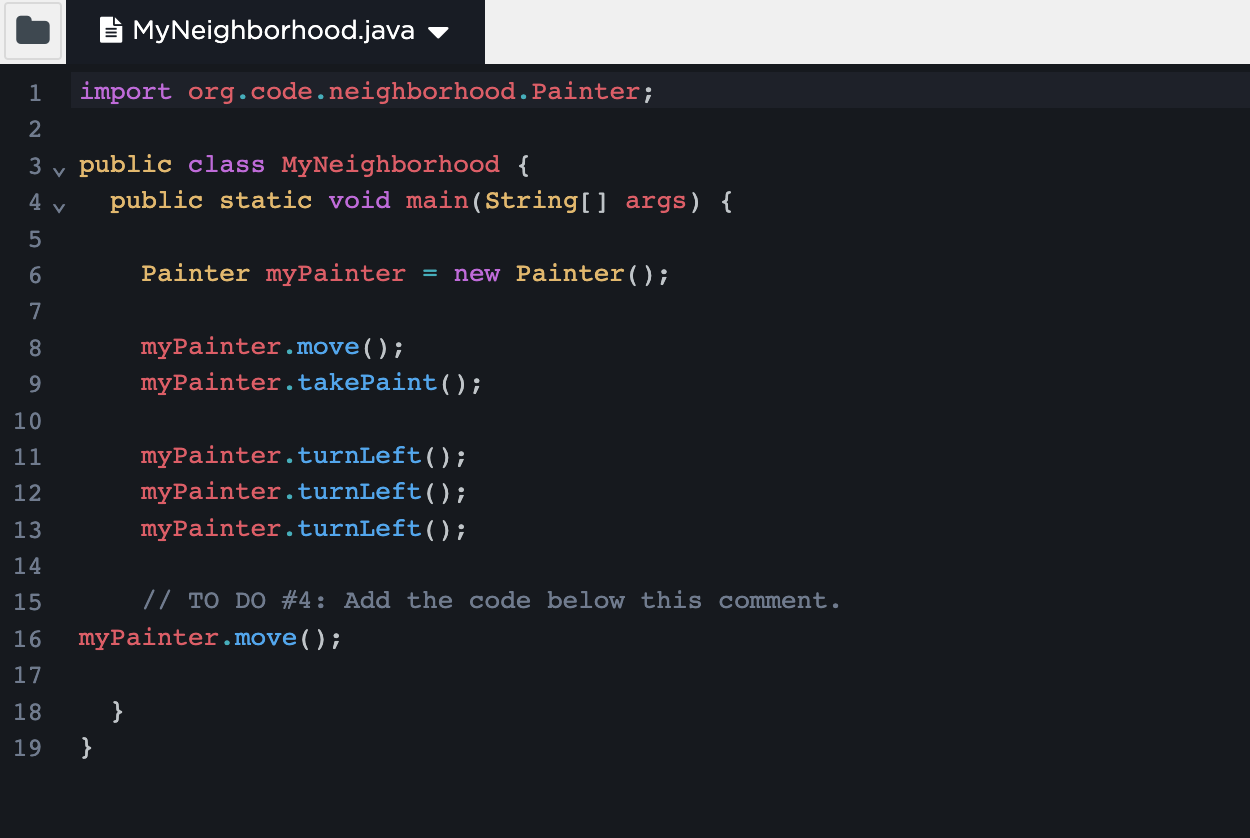
Key Learnings from Lesson 2
-
made a class and object
-
allowed the painter to move and take paint, then turn left
-
in other words, learned how to use different methods on the object
Lesson 3: The Neighborhood
- attribute - a characteristic of an object
- behavior - an action that an object can perform
- bug - an error in the code
- class - a programmer-defined blueprint from which objects are created
- constructor - a block of code that has the same name as the class and tells the computer how to create a new object
- debugging - finding and fixing problems in an algorithm or program
- instantiate - to call the constructor to create an object
- object - an instance of a class
- object-oriented programming - an approach to creating and using models of physical or imagined objects
- package - a collection of similar classes
- state - the attributes of an object that are represented by its instance variables
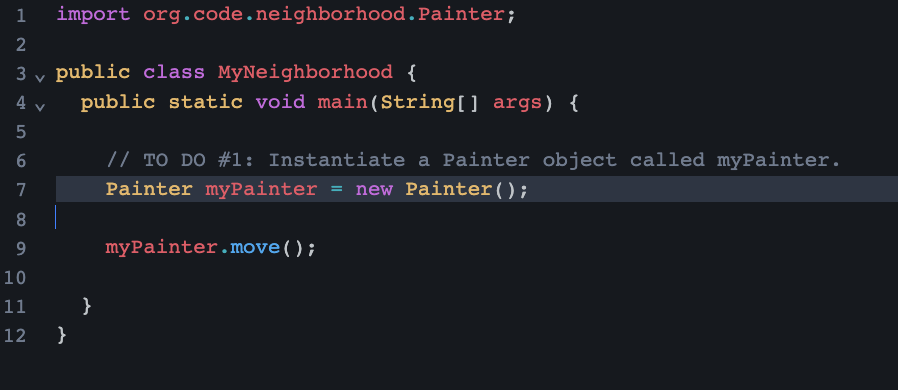
Key Learnings from Lesson 3
-
Blueprints define the attributes and behaviors than an object can have and can analyze Painter
-
Practiced creating Painter objects using the “new” keyword
Lesson 4: Navigating and Painting
- Procedural Abstraction - allows a programmer to use a method by knowing what the method does even if they do not know how the method was written
- void method - a method that performs an action but does not return a value
- argument - a value passed to a method or constructor when the method or constructor is called
- dot operator - used to call a method in a class
- method - a named set of instructions to perform a task
- parameter - a variable in the method or constructor signature that defines the type of value to receive when the - method or constructor is called
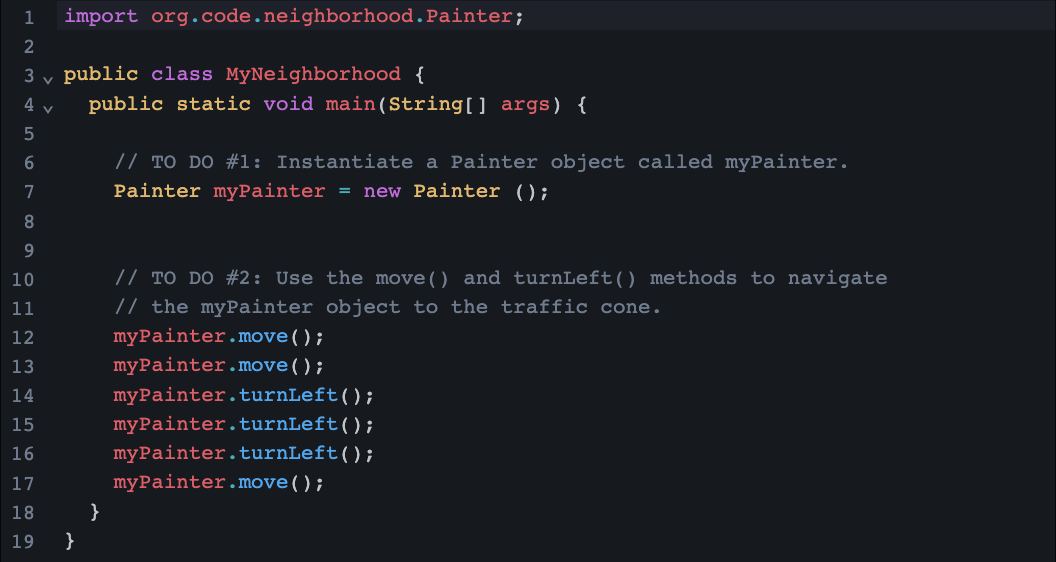
Key Learnings from Lesson 4:
-
Painter class has methods to navigate and paint the neighborhood
-
learned the syntax for calling methods
-
learned to debug syntax errors
Lesson 5: One-Way Selection Statements
- boolean - a primitive data type that can be either true or false
- if statement - a conditional statement that only executes when the condition is true
- condition - determines whether or not to execute a block of code
- conditional statement - a statement that only executes when a condition is true
- logic error - an error that occurs when the code runs but does not do what was expected
- return - to exit a method and go back to the point in the program that called it with the requested value or information

Key Learnings from Lesson 5
-
learning to use conditional statements in java
-
program can make decisions based on the current state of the Painter
-
Identifying strategies for debugging
Lesson 6: PainterPlus
- super keyword - a keyword used to refer to the superclass
- constructor signature - the first line of the constructor which includes the public keyword, the constructor name, and the values to specify when an object is created
- inheritance - an object-oriented programming principle where a subclass inherits the attributes and behaviors of a superclass
- subclass - a class that extends a superclass and inherits its attributes and behaviors
- superclass - a class that can be extended to create subclasses

Key Learnings From Lesson 6
-
needed to consider the need for designing specialized types of classes
-
learned about inheritance to create a new type of Painter called PainterPlus
-
learned how to add new behaviors to expand capabilities while using old
Lesson 7: Writing Methods
- method signature - consists of a name and parameter list
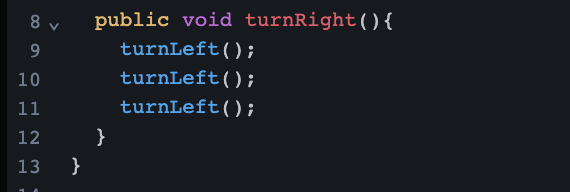
Key Learnings from Lesson 7
-
write and use a new void method in Painter Plus
-
new behaviors between superclasses and sunglasses to identity situations when to write new methods in the superclass versus in the subclass
Lesson 8: Code Reviews
- code review - the process of examining code and providing feedback to improve the quality and functionality of the program
- comment - a text note that is ignored by the compiler to explain or annotate the code
- documentation - written descriptions of the purpose and functionality of code
- programming style - a set of guidelines for formatting program code

Key Learnings from Lesson 8
-
// is comment for one line
-
/* */ is for comments spanning multiple lines
-
learning importance of code reviews to give and receive feedback
Lesson 9: Loops
- while loop - a control structure which executes a block of code repeatedly as long as a condition is true
- algorithm - a set of instructions to solve a problem or accomplish a task
- control structure - a conditional or iteration statement which affects the flow of a program
- efficient - getting the best outcome with the least amount of waste
- infinite loop - a loop where the Boolean expression always evaluates to true
- iteration statement (loop) - a control structure that repeatedly executes a block of code
- pseudocode - a plain language description of the steps in an algorithm

Key Learnings From Lesson 9
-
selection statements to execute if the condition is true
-
iteration using while loops
-
developing algorithms using selection statements and iteration along with implement our own algorithms
Lesson 10: Two-Way Selection Statements
- NOT ( ! ) operator - a logical operator that returns true when the operand is false and returns false when the operand is true
- if-else statement (two-way selection statement) - specifies a block of code to execute when the condition is true and a block of code to execute when the condition is false
- logical operator - an operator that returns a Boolean value
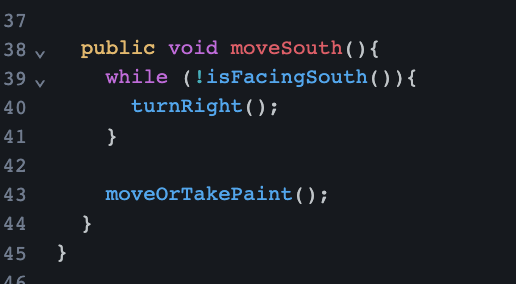
Key Learnings from Lesson 10
-
expanded knowledge of selection statements and Boolean expressions to use two way selection statements
-
NOT (!) logical operator
-
checked the state of an object and executed a specific set of instructions
Lesson 11: Debugging Strategies
- concatenation - joining two strings together
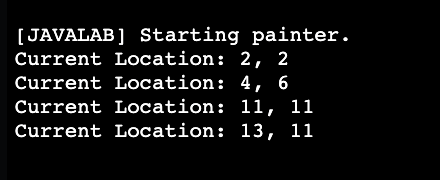
Key Learnings From Lesson 11
-
learned to print information in console as debugging tool
-
expand our PainterPlus to implement a new method that shows the state of the PainterPlus object
-
troubleshoot other errors
Lesson 12: Decomposition and Design
- Method Decomposition - the process of breaking a problem down into smaller parts to write methods for each part
- edge case - a bug that occurs at the highest or lowest end of a range of possible values or in extreme situations
- redundant code - code that is unnecessary

Key Learnings From Lesson 12
-
learned to write pseudocode to plan algorithms
-
Decomposition and top-down design to deconstruct problems into smaller tasks
-
Translate algorithms into methods and consider edge cases to improve programs
Lesson 13: PatternPainter
- inheritance hierarchy - where a class serves as a superclass for more than one subclass
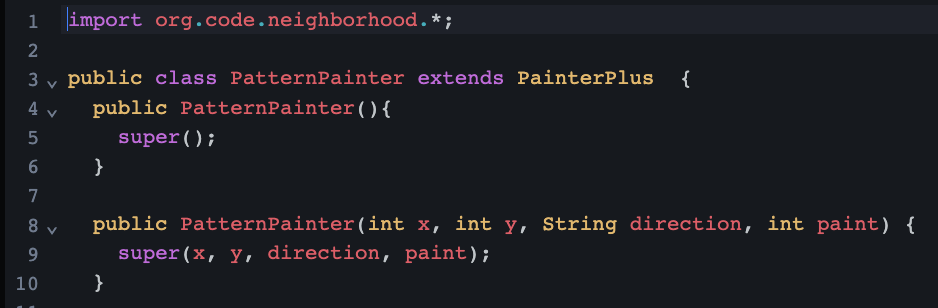
Key Learnings From Lesson 13
-
creating new types of painters with special behaviors
-
writing a new subclass that extends PainterPlus
-
practicing decomposition to develop new algorithms
-
Lesson 14: Background Painter

Key Learnings from Lesson 14
-
creating a new additional subclass that extends PainterPlus
-
practice using decomposition to develop algorithms
-
multiple objects in order to reach goal and help the painter
Lesson 15: Open Source Code
- open source code - code that is freely available for anyone to use, study, change, and distribute

Key Learnings from Lesson 15
-
examining open source code
-
connect real world application and concepts we have learned throughout this unit
-
review the characteristics of software engineers